Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
*; Mihara, Morihiro;
JNC TN8430 2001-007, 56 Pages, 2002/01
In the geological disposal concept of radioactive wastes, a kind of clay with sorption ability and low permeability, called bentonite, is envisaged as an engineered barrier system in the geological repository. Also, the cemetitious material is envisaged as the backfill material in the vaults and the structure material of the vaults. The groundwater in contact with the cementitious material will promote hyperalkaline conditions in the repository environment and these conditions will affect the performance of the bentonite. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the interaction between the cementitious material and the bentonite for the evaluation of long term stability of the disposal system. In this study, for the identification and the investigation of the secondary minerals, the batch immersion experiments of the powder bentonite were carried out using synthetic cement leachates (pH=7, 12.5, 14) at 200 C. As the results, it was confirmed that Na as exchangeable cations in the bentonite can exchange relatively easily with Ca in the solution from the experiment results. And the ratio of cation exchange was estimated to be about 25% based on the amount of exchangeable cations Ca
C. As the results, it was confirmed that Na as exchangeable cations in the bentonite can exchange relatively easily with Ca in the solution from the experiment results. And the ratio of cation exchange was estimated to be about 25% based on the amount of exchangeable cations Ca between layers. Furthermore, it was concretely shown that the generation of analcime might be affected by the Na concentration from results of the solution analyses and a stability analysis of analcime using the chemical equilibrium model, in addition to the pH in the solution.
between layers. Furthermore, it was concretely shown that the generation of analcime might be affected by the Na concentration from results of the solution analyses and a stability analysis of analcime using the chemical equilibrium model, in addition to the pH in the solution.
JNC TN8400 2001-008, 36 Pages, 2001/03
Research on geologic disposal of high-level radioactive waste(HLW) has been underway in many countries. Bentonite exhibiting a low permeability, high swelling property and high sorption capacity for many radioelements is proposed as a buffer material in many countlies. Recently, cementitious materials are considered as candidate matelials for the geologic disposal of high-level radioactive waste. As the pH and the Ca, Na, K contents of hyperalkaline pore water from the cementitious materials are high, this hyperalkaline pore water would alter the buffer material. The main aim of this study is to investigate the effect of alkaline pore water into the bentonite. Used materials are montmorillonite, albite and quartz composing bentonite. These minerals mixed in a constant ratio (1:1wt%) made to react to distilled water and the alkali solutions (pH11-13). These studies have been conducted at temperatures of 50 - 150 C and run times of 10 - 200 day. XRD(X-ray powder diffraction) and SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) analyses were applied to studying the structure and quantitative data of each sample. From the result of this study, the main formed mineral of this experiment was analcime, which showed the tendency with a large amount of generation at a higher pH and temperature. Quantitative data of this study was conducted by X-ray powder diffraction method. THe order of the amount of the second analcime in each experiment is shown in the following. Montmorillonite and albite mixing test
C and run times of 10 - 200 day. XRD(X-ray powder diffraction) and SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) analyses were applied to studying the structure and quantitative data of each sample. From the result of this study, the main formed mineral of this experiment was analcime, which showed the tendency with a large amount of generation at a higher pH and temperature. Quantitative data of this study was conducted by X-ray powder diffraction method. THe order of the amount of the second analcime in each experiment is shown in the following. Montmorillonite and albite mixing test  Montmorillonite test
Montmorillonite test  Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test Activation energies (E
Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test Activation energies (E ) using the quantitative data of each test are shown in the following. (1)Montmorillonite test : 54.9kJ/mol (2)Montmorillonite and albite mixing test : 51.9kJ/mol (3)Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test : 59.6kJ/mol
) using the quantitative data of each test are shown in the following. (1)Montmorillonite test : 54.9kJ/mol (2)Montmorillonite and albite mixing test : 51.9kJ/mol (3)Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test : 59.6kJ/mol
Mine, Tatsuya*; Mihara, Morihiro;
JNC TN8430 2000-010, 27 Pages, 2000/07
In the geological disposal system of the radioactive wastes, gas generation by microorganism could be significant for the assessment of this system, because organic material included in groundwater, buffer material and wastes might serve as carbon sources for microorganisms. In this study, gas generation tests using microorganisms were carried out under anaerobic condition. The amount of methane and carbon dioxide that were generated by activity of Methane Producing Bacteria (MPB) were measured with humic acid, acetic acid and cellulose as carbon sources. The results showed that methane was not generated from humic acid by activity of MPB. However, in the case of using acetic acid and cellulose, methane was generated, but at high pH condition (pH=10), the amount of generated methane was lower than at low pH (pH=7). It was not clear whether the pH would affect the amount of generated carbon dioxide.
Mine, Tatsuya*; Mihara, Morihiro;
JNC TN8430 2000-009, 35 Pages, 2000/07
In the geological disposal system of TRU wastes, nitrogen generation by denitrifying bacteria could provide significant impact on the assessment of this system, because nitrate contained in process concentrated liquid waste might be electron acceptor for denitrifying bacteria. In this study, the activities and tolerance of denitrifying bacteria under disposal condition were investigated. pseudomonas denitrificans as denitrifying bacteria was used. The results showed that Pseudomonas denitrificans had activity under reducing condition, but under high pH condition (PH 9.5), the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans was not detected. It is possible that the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans would be low under disposal condition.
9.5), the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans was not detected. It is possible that the activity of Pseudomonas denitrificans would be low under disposal condition.
Fukunaga, Sakae*; Yokoyama, Hidekazu*; Arai, Kazuhiro*; Asano, Hidekazu*; Senjyu, Takafumi*; Kudo, Akira*
JNC TJ8400 2000-030, 54 Pages, 2000/02
It is easy to assume from the past data that microbial transport do not find at 100%-sodium bentonite. Microbial transport do not find at 100%-calcium bentonite too. There are no effects to distribution ration (Kd) of Neptunium (Np) and Plutonium (Pu) with bentonite by sterilizing on low Eh condition (Eh= -500mv). Kd values of Np and Pu show behavior, which are increasing on the hard acidic and alkali conditions. Especially, Kd values of Pu shows one of Kd value is about 100 ml/g on pH=3 6, but the other of Kd value is about 400,000 ml/g on pH=13. Precipitating plutonium hydrates occurred the large Kd value on alkali condition.
6, but the other of Kd value is about 400,000 ml/g on pH=13. Precipitating plutonium hydrates occurred the large Kd value on alkali condition.
Fukunaga, Sakae*; Yokoyama, Hidekazu*; Arai, Kazuhiro*; Asano, Hidekazu*; Senjyu, Takafumi*; Kudo, Akira*
JNC TJ8400 2000-029, 36 Pages, 2000/02
It is easy to assume from the past data that microbial transport do not find at 100%-sodium bentonite. Microbial transport do not find at 100%-calcium bentonite too. There are no effects to distribution ration (Kd) of Neptunium (Np) and Plutonium (Pu) with bentonite by sterilizing on low Eh condition (Eh = -500mv). Kd values of Np and Pu show behavior, which are increasing on the hard acidic and alkali conditions. Especially, Kd values of Pu shows one of Kd value is about 100 ml/g on pH = 3 6, but the other of Kd value is about 400,000 ml/g on pH = 13. Precipitating plutonium hydrates occurred the large Kd value on alkali condition.
6, but the other of Kd value is about 400,000 ml/g on pH = 13. Precipitating plutonium hydrates occurred the large Kd value on alkali condition.
Tomari, Haruo*; *; Shimogori, Kazutoshi*; Wada, Ryutaro*; ; Taniguchi, Naoki
JNC TN8400 99-076, 100 Pages, 1999/10
Effects of bentonite clay, applied potential, pH, of solution and cathodic polarization time on hydrogen absorption into titanium, which is one of the candidate materials of overpack for high-level radioactive waste container, have been investigated in artificial underground water. Considering the result at various test time and assuming the hydrogen absorption is ruled by the paraboric law, the amount of hydrogen after 1000 years exposure calculated to about 17ppm, which will be absorbed at the applied potential of -0.51 vs. SHE corresponds to equilibrium potential of hydrogen. It seems the assumption of the parabolic law and the test period are proper, because the linear relations were obtained between the amount of absorbed hydrogen and the logarithm of the averaged cathodic current and between the slopes of the lines and a square root of the test time. Titanium seems to have a life over 1000 years in deep underground repository according to assumption that about 500ppm absorbed hydrogen is critical for hydrogen embrittlement of titanium.
; ; Sato, Haruo; Shibata, Masahiro
JNC TN8400 99-088, 58 Pages, 1999/06
Sorption and diffusion behavior of palladium, which has been identified as one of the hazardous radionuclides in performance assessment of HLW disposal, in bentonite, granodiorite and tuff was studied in order to make reliable data set for the performance assessment. Sorption experiments of Pd on bentonite, granodiorite and tuff were conducted as functions of pH, ionic strength and liquid to solid ratio by batch method under aerobic conditions at room temperature. The distribution coefficients (K ) of Pd on these solids were almost in the range of 10
) of Pd on these solids were almost in the range of 10 to 10
to 10 m
m /kg and were in the order of bentonite
/kg and were in the order of bentonite  granodiorite
granodiorite  tuff. The sorption trends with change in PH, ionic strength and liquid to solid ratio are very similar between three solids. The K
tuff. The sorption trends with change in PH, ionic strength and liquid to solid ratio are very similar between three solids. The K values were the highest at pH5 and decreased with increasing pH between 5 and 11. The effect of ionic strength on K
values were the highest at pH5 and decreased with increasing pH between 5 and 11. The effect of ionic strength on K was not found in a range of 10
was not found in a range of 10 to 10
to 10 , but K
, but K values increased with increasing liquid to solid ratio. The width of variation in K
values increased with increasing liquid to solid ratio. The width of variation in K was one order of magnitude in a liquid to solid ratio of 0.1 to 1 m
was one order of magnitude in a liquid to solid ratio of 0.1 to 1 m /kg. Sorption behavior of Pd is different from that of divalent metal ions such as Ni and Co etc. and chemical analogy may be inappropriate. The dominant aqueous species of Pd in the expermental conditions studied is estimated to be neutral species, Pd(OH)
/kg. Sorption behavior of Pd is different from that of divalent metal ions such as Ni and Co etc. and chemical analogy may be inappropriate. The dominant aqueous species of Pd in the expermental conditions studied is estimated to be neutral species, Pd(OH) (aq) by the thermodynamic calculations. The K
(aq) by the thermodynamic calculations. The K values of Pd on three solids were relatively high and uncharged complexes may be more strongly sorbed. The pH dependency of K
values of Pd on three solids were relatively high and uncharged complexes may be more strongly sorbed. The pH dependency of K values suggests that Pd sorption is most likely to be occurring onto positively charged S-OH
values suggests that Pd sorption is most likely to be occurring onto positively charged S-OH type site which are progressively removed (to from SOH and SO
type site which are progressively removed (to from SOH and SO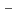 sites) at higher pH values. Diffusion behavior of Pd in bentonite was also studied by in-diffusion method as a function of dry density. The D
sites) at higher pH values. Diffusion behavior of Pd in bentonite was also studied by in-diffusion method as a function of dry density. The D values obtained based on the instantaneous planar source model were in the orders of ...
values obtained based on the instantaneous planar source model were in the orders of ...
PATRICIA F SALTE*; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Apted, M. J.*; Yui, Mikazu
JNC TN8400 99-023, 231 Pages, 1999/05
The groundwater chemistry is one of important geological environment for performance assessment of high level radioactive disposal system. This report describes the results of geostatistical analysis of groundwater chemistry in Japan. Over 15,000 separate groundwater analyses have been collected of deep Japanese groundwaters for the purpose of evaluating the range of geochemical conditions for geological radioactive waste repositories in Japan. The significance to issues such as radioelement solubility limits, sorption, corrosion of overpack, behavior of compacted clay buffers, and many other factors involved in safety assessment. It is important therefore, that a small, but representative set of groundwater types be identified so that defensible models and data for generic repository performance assessment can be established. Principal component analysis (PCA) is used to categorize representative deep groundwater types from this extensive data set. PCA is a multi-variate statistical analysis technique, similar to factor analysis or eigenvector analysis, designed to provide the best possible resolution of the variability within multi-variate data sets. PCA allows the graphical inspection of the most important similarities (clustering) and differences among samples, based on simultaneous consideration of all variables in the dataset, in a low dimensionality plot. It also allows the analyst to determine the reasons behind any pattern that is observed. In this study, PCA has been aided by hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA), in which statistical indices of similarity among multiple samples are used to distinguish distinct clusters of samples. HCA allows the natural, a priori, grouping of data into clusters showing similar attributes and is graphically represented in a dendrogram Pirouette is the multivariate statistical software package used to conduct the PCA and HCA for the Japanese groundwater dataset. An audit of the initial 15,000 sample dataset on the ...
Oda, Chie; *
JNC TN8400 98-001, 14 Pages, 1998/11
Solubilities of amorphous stannic oxide, SnO (am) in Na-ClO
(am) in Na-ClO -Cl-SO
-Cl-SO aqueous systems were measured to quantitatively investigate the influences of the ligands OH
aqueous systems were measured to quantitatively investigate the influences of the ligands OH , Cl
, Cl and SO
and SO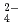 on solubilities. They were also measured in bentonite equilibrated solutions to discuss the behavior of tin under a repository condition of a high-revel radioactive waste. The solubility data in sodium perchlorate media in the range of pH from 6 to 11 showed pH dependency, and the hydrolysis constants of tin (IV) were determined (Amaya, et al., 1997). No significant changes in solubilities with the variation in Cl
on solubilities. They were also measured in bentonite equilibrated solutions to discuss the behavior of tin under a repository condition of a high-revel radioactive waste. The solubility data in sodium perchlorate media in the range of pH from 6 to 11 showed pH dependency, and the hydrolysis constants of tin (IV) were determined (Amaya, et al., 1997). No significant changes in solubilities with the variation in Cl , SO
, SO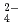 concentrations were observed in Na-ClO
concentrations were observed in Na-ClO -Cl-SO
-Cl-SO aqueous systems, so this indicates that chloride and sulfate species were less effective than hydroxide complexes. On the other hand, solubilities in bentonite equilibrated solutions were higher than solubilities of other experiments in simple systems. These results suggest that (1) other complexes of tin except hydroxide, chloride or sulfate complexes of tin (IV) may dominantly exist in aqueous phase, (2)solid phase other than SnO
aqueous systems, so this indicates that chloride and sulfate species were less effective than hydroxide complexes. On the other hand, solubilities in bentonite equilibrated solutions were higher than solubilities of other experiments in simple systems. These results suggest that (1) other complexes of tin except hydroxide, chloride or sulfate complexes of tin (IV) may dominantly exist in aqueous phase, (2)solid phase other than SnO (am) may limit the solubility of tin under repository conditions.
(am) may limit the solubility of tin under repository conditions.